These are Ancient Greek words you should be familiar with in order to get the best marks in your exam.
Acropolis - A fortified hill within Athens. The Acropolis was the site of many important ceremonies, and was home to the Parthenon.

Agora - The Athenian marketplace.

Archon - The Greek name for the magistrates, which you will learn about in the Citizenship section of Ancient Athenian Power and Freedom.
Attica - Attica was an Ancient geographical area which included Athens. By the 6th Century BCE, after the reforms of Cleisthenes, Attica was fully governed by Athens, and the other small towns within Attica didn't have any independence. In some ways, Athens could be compared with London, and Attica with England.
Boule - The Greek name for the Council of 500, which you will also learn about in the Citizenship section of Ancient Athenian Power and Freedom.
Drachma – A drachma was a silver coin, used to buy goods and services in Ancient Athens. One drachma was worth six obols.

Metic - The Greek name for a foreigner who lived in Athens. A metic was anyone who didn’t have two Athenian parents. A child of a metic born in Athens would still be a metic, since both of their parents weren’t Athenian.
Obol – An obol was a silver coin, used to buy goods and services in Ancient Athens.

Strategoi - The Greek name for the generals, which you will learn about in the Citizenship section of Ancient Athenian Power and Freedom.
Pnyx - A hill within Athens. The Pnyx was where the Assembly met.
Polis - Translated into English as a “city-state”. The plural of polis is poleis. These were the major political bodies in Ancient Greece – they had similar powers to govern themselves as countries do today, but were usually much smaller. Thebes, Corinth, Sparta and, of course, Athens, are all examples of poleis.
Pyrtaneis - The group that led the Boule. The Pyrtaneis were comprised of 50 men from one of the ten tribes, and were changed every month.
Strategoi - The Greek name for the Athenian generals, which you will learn about in the Citizenship section of Ancient Athenian Power and Freedom.
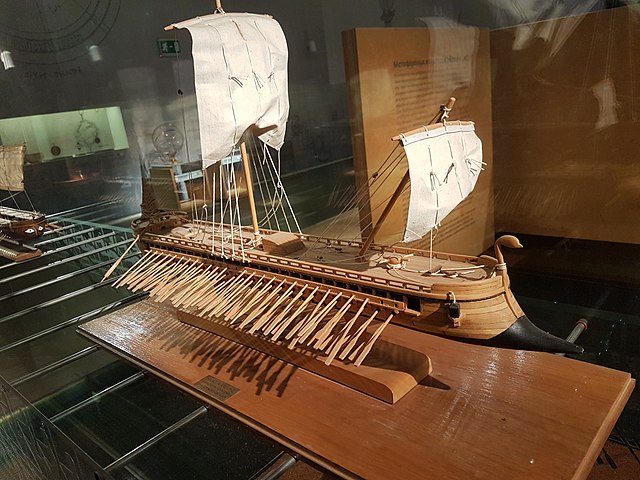
Trireme - Ancient Mediterranean war ships. Triremes were wooden, with a bronze-sheathed prow that was used to ram into enemy ships. They had three lines of rowers on either side of the ship. The Athenian navy was made up of triremes.

Tyrannos - Ancient Greek word for tyrant. In Ancient Greece, a tyrant was not necessarily a bad ruler who extorted and threatened his citizens. A tyrant was simply someone with absolute power over their nation, and could have been a good or bad ruler.